Variable Inverter/Rectifier/Transformer
A Variable-Inverter-Rectifier-Transformer (VIRT) is used in power converter circuits and magnetic circuit structures, including grid-interfaced chargers, isolated DC-DC converters, grid-interfaced inverters for photovoltaics, DC-AC converters for uninterruptible power supplies, and AC-AC converters for solid state transformers.
Researchers
-
variable inverter/rectifier/transformer
United States of America | Granted | 12,051,980 -
variable inverter/rectifier/transformer
United States of America | Granted | 11,716,030
Figures
Technology
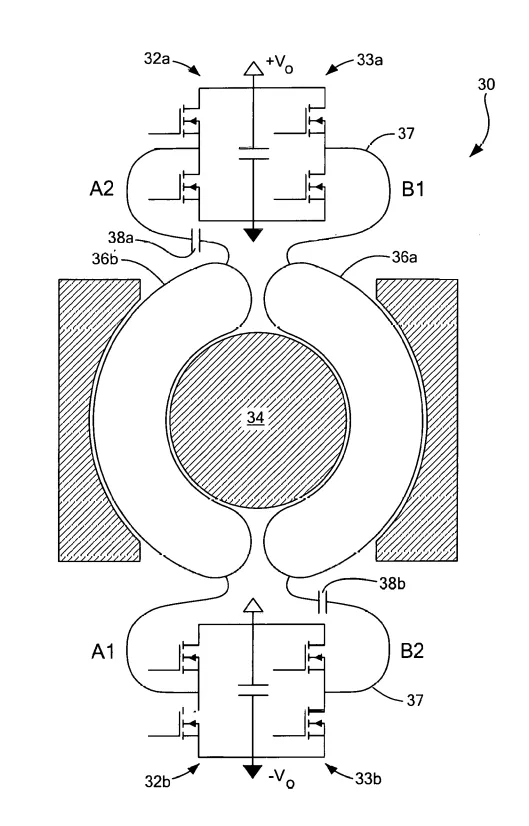
The invented VIRT includes a fractional, reconfigurable effective turns ratios for a transformer. This structure yields AC currents flowing in only fractions of a complete turn prior to rectification, enabling reduced conduction loss as compared to previous designs. The VIRT comprises a series of switching cells distributed around a magnetic core and coupled to half-turns wound through that core. By controlling operating modes of the switching cells, it is possible to control over flux paths and current paths in the transformer. The VIRT is valuable in converters with wide operating voltage ranges and high step-up/down, as it offers a means of reducing turns count and copper loss within a transformer while facilitating voltage doubling and quadrupling. The fractional turns also enable planar transformers which offer potential for improved fabrication and miniaturization, especially on a printed circuit board.
Problem Addressed
Transformers are key components to power transfer in converters but limit the size reduction and efficiency due to the challenges in implementing fractional turns in conventional transformers and in requirement of large turns ratio. A fractional turn transformer enables reduced turn counts in planar magnetics where core window breadth is maximized while offering the preferred trade-off between copper loss and core loss. Past “fractional turn” design concepts may have fractionalized the amount of flux linked by windings but still imposing significant conduction losses and parasitic inductances. There has been a demand for a true fractional turn transformer which achieves miniaturization in power electronics.
Advantages
- Optimized loss; balanced between core loss and copper loss
- Enables improved fabrication techniques including printed circuit board manufacturing processes
- Removes limitations on power conversion ratios; allows efficient low voltage, high current applications
Publications
Ranjram, M. K., Moon, I., Perreault, D. J. (2018). Variable-Inverter-Rectifier-Transformer: A Hybrid Electronic and Magnetic Structure Enabling Adjustable High Step-Down Conversion Ratios. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 33(8), 6509-6525. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPEL.2018.2795959.
License this technology
Interested in this technology? Connect with our experienced licensing team to initiate the process.
Sign up for technology updates
Sign up now to receive the latest updates on cutting-edge technologies and innovations.