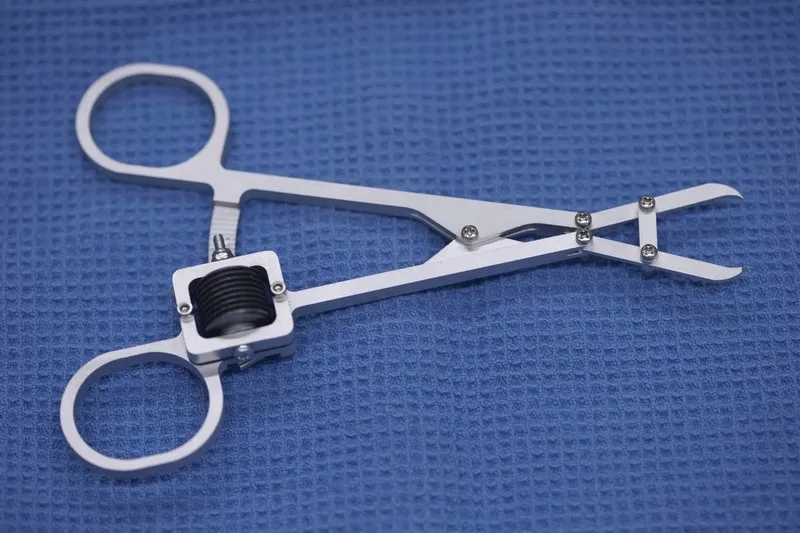
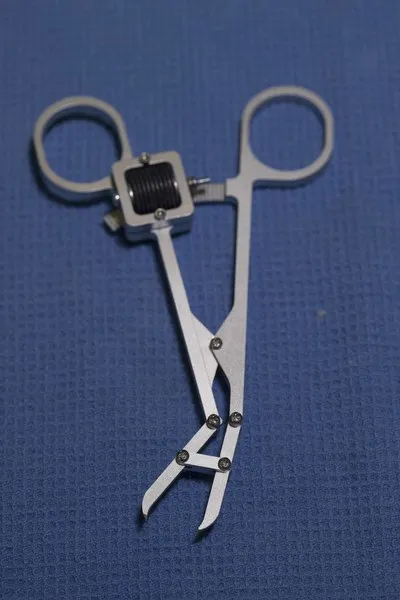
Bone Reduction Forcep Allowing for Both Continuous and Discrete Adjustment
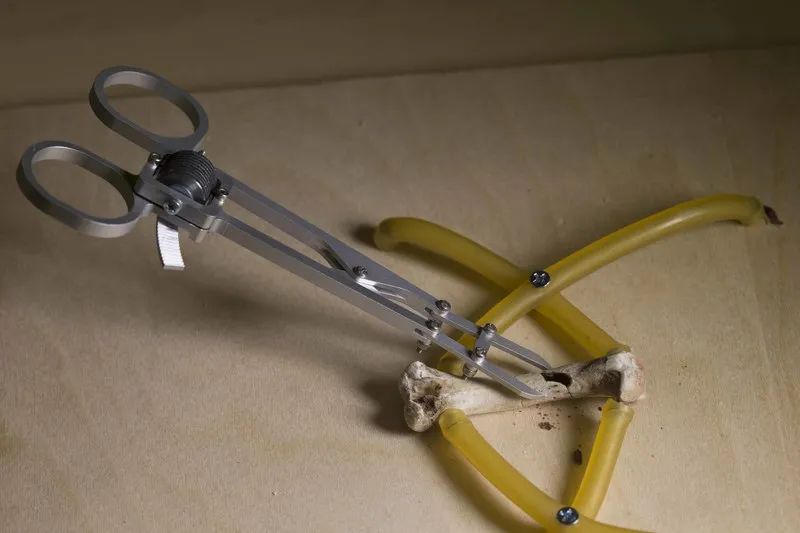
This invention is a forcep design that allows both continuous and discrete force adjustment and an extra degree of freedom to provide quicker and more stable anatomic alignment in fracture reduction.
Researchers
-
bone reduction forceps
United States of America | Granted | 10,925,655
Figures
Technology
This invention has three design features to improve surgical outcomes. First, a clutchable worm and rack locking mechanism allows for fine control as well as gross adjustment over the tightening and loosening of the forceps. Current devices increase clamping force in discrete intervals and, when released, release all of their force at once. Alternatively, existing fine control mechanisms allow for sensitive control to achieve proper anatomic alignment, but are slow and cumbersome to use, and often do not allow for a desirable “complete release” feature. This design combines the best of both aspects, allowing a surgeon to achieve gross control for rapid alignment, with the added benefit of fine control when needed. Second, this technology contains a five-bar linkage which provides an increased mechanical advantage and as well as an additional degree of freedom for improved surgical control. Lastly, this design can incorporate a wide variety of interchangeable tips to reduce the number of tools necessary in a surgical suite. These three design features can be incorporated entirely independent of one another and can each be independently incorporated into existing reduction forcep architectures.
Problem Addressed
Existing bone reduction forceps, used in over 200,000 hand surgeries annually, do not allow sufficiently fine adjustment of the clamping force resulting in longer, more difficult procedures, increasing the risk of further bone breaking, anesthesia complications, misunion, or nonunion. This invention is a forcep design that allows both continuous and discrete force adjustment and an extra degree of freedom to provide quicker and more stable anatomic alignment in fracture reduction. This forcep design may be used for hand reduction surgery or generalized to forceps for larger bones and other surgical tools.
Advantages
- Continuous and discrete adjustment
- Increased mechanical advantage
- Additional degree of freedom
- Interchangeable tips reduce cost and variety of tools needed to supply a surgical suite
License this technology
Interested in this technology? Connect with our experienced licensing team to initiate the process.
Sign up for technology updates
Sign up now to receive the latest updates on cutting-edge technologies and innovations.