RNA-Loaded Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP)
This technology provides pharmaceutical compositions for self-replicating RNA (repRNA) vaccines with an inhibitory nucleic acid, delivered through lipid nanoparticles for enhanced immunity in the patient. Vaccines may be designed to combat any number of infections including HIV, COVID-19, and certain cancers.
Researchers
-
rna-loaded lipid nanoparticles
Patent Cooperation Treaty | Published application -
rna-loaded lipid nanoparticles
United States of America | Pending -
rna-loaded lipid nanoparticles
Australia | Pending -
rna-loaded lipid nanoparticles
Canada | Pending
Figures
Technology
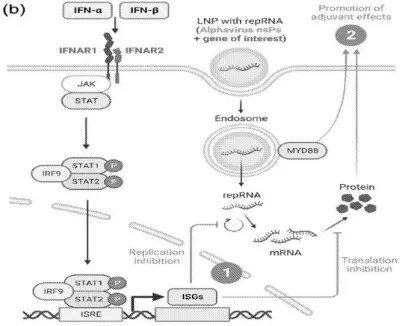
Through vaccines or similar pharmaceutical compositions, this technology delivers repRNA (encoded with an antigen gene of interest) and inhibitory nucleic acid to immune cells by means of small particles composed of lipids. Upon administration to the subject, the nucleic acid binds to a segment of Ifnar1 to prevent its expression. This allows immune cells to produce the encoded antigen and elicit a robust antibody response.
Problem Addressed
Unlike traditional vaccines, RNA vaccines are encoded with mRNA (genetic sequences for specific antigens), allowing the immune system to recognize and combat pathogens without introducing any infectious elements into the system. Advancements in this technology have led to the use of repRNA, which encodes antigen genes and the genes for RNA replication, eliciting a more robust and long-lasting immune response. This is done by altering an RNA virus so that the viral genes are replaced with the antigen gene of interest. However, this structure can trigger the immune system to suppress repRNA translation and replication. To overcome these challenges, this new composition includes key genetic information on protein synthesis in the form of inhibitory nucleic acids designed to silence Ifnar1— the gene responsible for the unwanted immune responses, permitting higher levels and more prolonged expression of the repRNA to provide lasting immunity for patients.
Advantages
-
repRNA vaccines are a safer and more effective method of eliciting immunity than traditional vaccines, as they remove the need for pathogen cultures and require only the target antigens gene sequence.
-
repRNA produces longer-lasting immunity than other vaccine alternatives
Publications
Kim, B., et al. "Optimization of storage conditions for lipid nanoparticle-formulated self-replicating RNA vaccines." Journal of Controlled Release Volume 353 (2023): 241-253. ISSN 0168-3659. Accessed February 14, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.11.022.
License this technology
Interested in this technology? Connect with our experienced licensing team to initiate the process.
Sign up for technology updates
Sign up now to receive the latest updates on cutting-edge technologies and innovations.