Method for Internal Wound Healing
This invention presents ingestible origami robots that can be controlled to move, manipulate, and accomplish clinically relevant tasks, such as removing a foreign body and patching a wound in the stomach.
Researchers
-
origami robots, systems, and methods of treatment
United States of America | Granted | 11,304,767 -
origami robots, systems, and methods of treatment
United States of America | Granted | 10,470,799
Figures
Technology
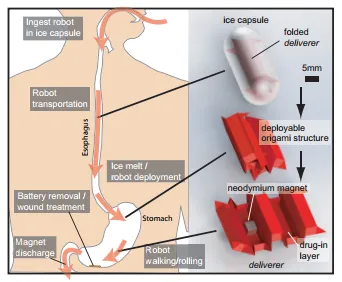
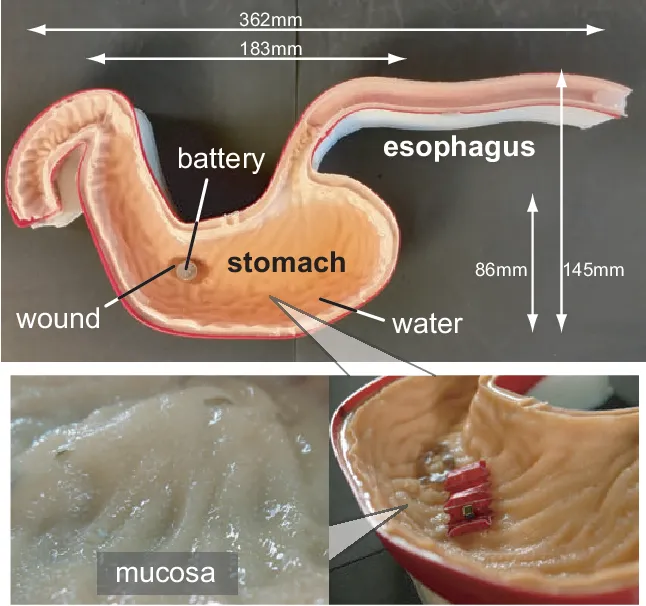
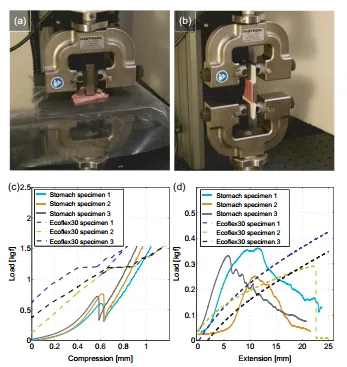
The inventors have developed a biocompatible and biodegradable origami robot that can be swallowed to perform simple procedures in the stomach without any incisions or external tethers. Once in the stomach, the robot self-deploys and uses its body to patch a wound, such as an inflammation made by an accidentally swallowed button battery. The inventors have used the origami design to fold and embed the robot in an ice capsule which can be swallowed, carried to the stomach and deployed. It is there actuated by external magnetic fields and guided to the location of the battery where it dislodges the battery from the inflammation site. Using an artificial stomach, the position of the robot was visually observed, though in real clinical applications, Hall-effect sensors, a combination of ultrasound, and X-rays would be employed to determine the position. The ice dissolution approach enhances the probability of a proper attachment, as the magnet steadily reorients itself while the ice melts to maximize connection strength. This approach also reduces the risk of the magnet and the battery magnetically pinching the mucosa. After the battery and the robot are removed from the body through the GI tract, the patient swallows another ice capsule-enclosed-origami robot. This second robot walks across the stomach wall and patches the inflammation site by releasing a drug to the damaged area as it degrades.
Problem Addressed
There has been considerable progress in interventional technologies for the gastrointestinal tract; large efforts are being directed towards microsurgical tools that are minimally invasive, biocompatible and biodegradable, multifunctional, and well accepted by the patient's immune system. One example of a clinical intervention where a multifunctional miniature robot is desired is the ingestion of button batteries. According to the National Capital Poison Center, more than 3500 people ingest batteries in the United States every year. 42 deaths and 169 cases with severe esophageal burns and subsequent complications have been reported. Considering the fatality of these accidents and the limited availability of efficient interventional tools to counteract them, the inventors approached this problem by deploying a miniature surgical robot in the stomach that can perform versatile medical and surgical tasks in vivo. Their approach requires no on-board electronics, allowing for a simple and minimally invasive robot, and a greater choice of biocompatible and biodegradable materials from which to fabricate them.
Advantages
- Ingestible, controllable, biodegradable and biocompatible origami robot for patching stomach wounds and removing foreign objects
- Concept of ice encapsulated deployable robot for safe transportation into the stomach
- Integrated drug delivery layer within the origami robot design
- External electromagnetic actuation system to remotely actuate the robots and the ice capsules
Publications
Miyashita, S., et al. "Ingestible, controllable, and degradable origami robot for patching stomach wounds," 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 2016, pp. 909-916. doi: 10.1109/ICRA.2016.7487222.
MIT News Office. "Ingestible Origami Robot." May 12, 2016.
License this technology
Interested in this technology? Connect with our experienced licensing team to initiate the process.
Sign up for technology updates
Sign up now to receive the latest updates on cutting-edge technologies and innovations.