Pre-Fever Detection of Infection
These are methods for detecting pathogen exposure before symptoms become apparent. This detection could lead to earlier patient care and increase the probability of a positive prognosis. These methods may help to reduce transmission during infectious disease outbreaks by enabling monitoring patient exposure without patient isolation or contact tracing. They may also have applications in the clinical setting, helping to treat post-operative or critical care patients well before they present with symptoms such as viremia, bacteremia, or sepsis.
Researchers
-
methods and systems for pre-symptomatic detection of exposure to an agent
United States of America | Granted | 10,332,638
Figures
Technology
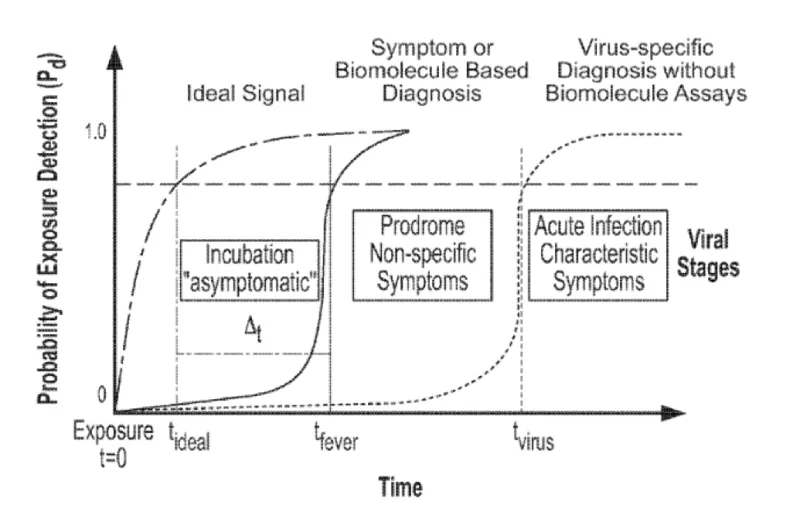
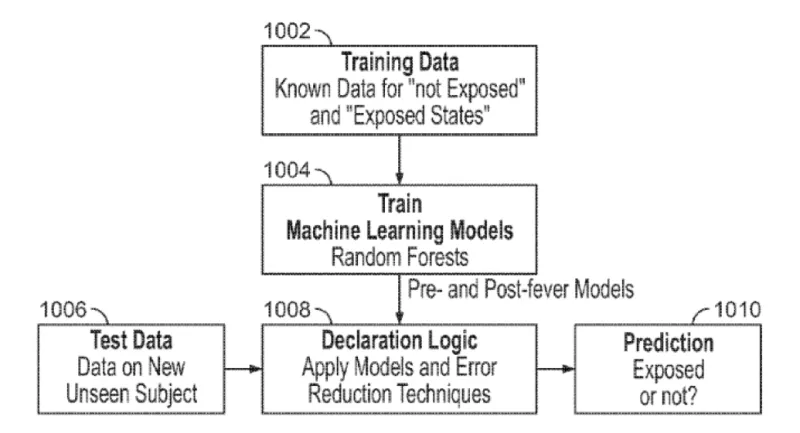
These techniques provide early warning of infection by monitoring physiological states before symptoms become apparent. Using machine learning models, these methods train classifiers with non-invasive patient data of physical waveforms, such as those from electrocardiography, hemodynamics, and temperature. They then apply those classifiers over a number of time intervals when analyzing an unknown patient’s data. Either the number of predictive patient state classifications or an aggregated patient state classification can then be used to indicate whether a patient has been exposed to an infectious or chemical agent. These are techniques with high sensitivity and low specificity.
Problem Addressed
Current state-of-the-art techniques for detecting pathogen exposure often utilize molecular diagnostics. These methods suffer from steep logistic burdens and associated costs. They are rarely used until patients self-report or present symptoms. Less demanding techniques exist that process patients’ physiological signals for the early detection of infection. However, these techniques utilize strongly-confounded signals such as heart rate, fever, and body core temperature. There is a need for technologies, such as these, that are capable of accurately processing traditionally confounded physiological signals to indicate whether a patient has been exposed to a viral infection, bacterial infection, or other communicable pathogens.
Advantages
- Pre-symptomatic indication
- Capable of processing simple physiological signals
- Can be used in public health or hospital settings
License this technology
Interested in this technology? Connect with our experienced licensing team to initiate the process.
Sign up for technology updates
Sign up now to receive the latest updates on cutting-edge technologies and innovations.