Gastric Residence Electronics
Long-term biomedical electronics in the human body can provide advanced diagnostic and therapeutic solutions. This invention is a device that is ingested and maintains long-term wireless communication while in the stomach, without the need for any invasive procedures or surgery. This invention is not limited to biomedical applications; it can be used for the defense, sports performance monitoring, and livestock and veterinary industries.
Researchers
-
gastric resident electronics
United States of America | Published application -
gastric resident electronics
United States of America | Granted | 11,684,315 -
gastric resident electronics
Australia | Granted | 2,018,375,145 -
gastric resident electronics
Canada | Published application -
gastric resident electronics
European Patent Convention | Published application -
gastric resident electronics
Japan | Granted | 7,394,775
Figures
Technology
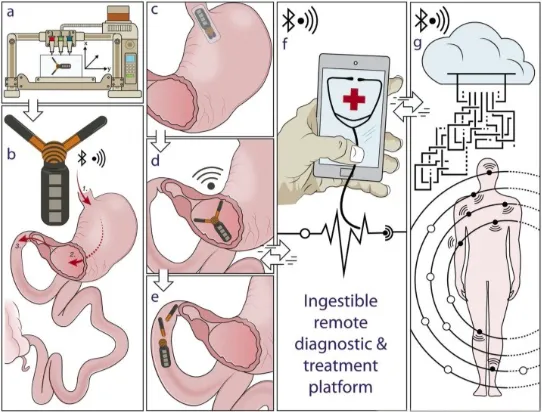
This invention is a combination of both a device and its methodology.
Device:
-
Made of 3D-printed layers of elastomeric and biocompatible polymer.
-
Stable in acidic environments and strong enough to sustain functions throughout the GI tract.
-
Integrated with a power system to drive its sensors and personalized drug delivery reservoirs as well as its communications and control system.
-
The re-configurable structure allows a change in format from an ingestible pill to an expanded retention form within the stomach. The change in structure is triggered upon dissolution of its water-soluble exterior gelatin capsule that effectively increases the device’s diameter to prevent passing into the small intestine.
Methodology:
-
Once the GRE is ingested and expanded, the device can communicate information, monitor an individual’s vital signs through sensors, and deliver personalized drugs.
-
The GRE is compatible with personal devices, such as smart phones, and empowers users to directly communicate and control the long-residence device without specialized equipment. This feature allows for seamless interconnection with other wireless electronics peripherals, wearable devices, and biomedical implants, enabling real-time feedback-based automated treatment or responsive mediation.
-
The device can connect to the digital cloud via personal electronics enabling remote health management and monitoring, including data collections supporting clinical studies and compliance.
-
Once the desired period of residence is over, the GRE disintegrates and safely passes through from the gastric space.
Problem Addressed
Most long-term human body electronics must be implanted through invasive procedures, and require a specialized receiver to communicate. Ingestible electronics have numerous useful functions, such as monitoring temperature, pH, and pressure, and the devices can include biomolecular sensors, wireless identification microchips, gas sensors, cameras for wireless imaging and endoscopy, and modules for drug delivery. However, they are generally incapable of maintaining a stable long-residence in the stomach. The Gastric Resident Electronics (GRE) is free of such problems because it is ingestible, maintains numerous functionalities, and has the stability to reside in the stomach long-term.
Advantages
- Does not require invasive procedures for long-term residence inside the body.
- Can be tailored and optimized via 3D-printing to achieve a desired residence period, including distinct geometry requirements of the organ.
- Can be administered orally, rectally, vaginally, nasally, or urethrally.
Publications
Yong Lin Kong, et al. 3D-Printed Gastric Resident Electronics. Advanced Materials Technologies. 2018 Dec 13. doi: 10.1002/admt.201800490
License this technology
Interested in this technology? Connect with our experienced licensing team to initiate the process.
Sign up for technology updates
Sign up now to receive the latest updates on cutting-edge technologies and innovations.