Dysferlinopathy Compounds
The objective of this technology is to treat dysferlinopathy, a group of rare muscular diseases including limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2b and Miyoshi myopathy. This technology is of interest to companies in the pharmaceutical and healthcare industries.
Researchers
-
compositions and methods for treating dysferlinopathy
United States of America | Pending
Figures
Technology
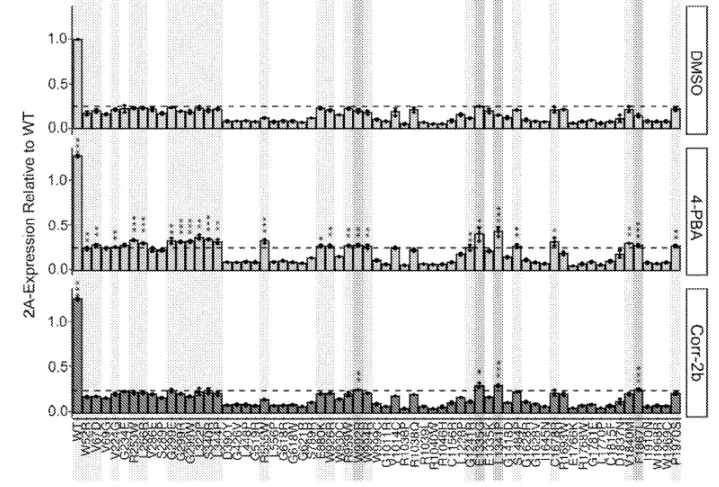
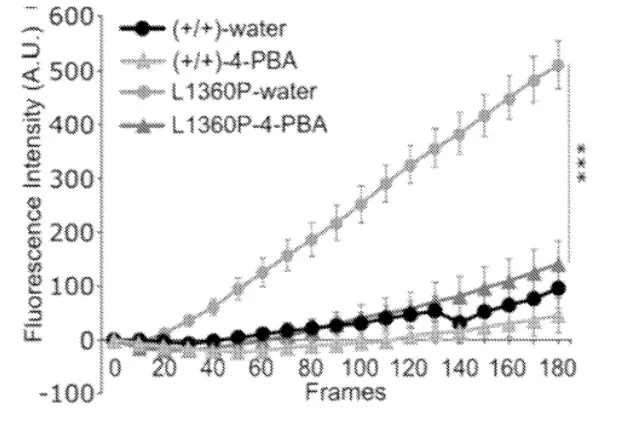
The technology consists of two compounds that have been determined to have potential in future treatments of dysferlinopathy. One of these compounds is Corr-2b, a compound classified as a cystic fibrosis corrector. In in vitro human dysferlinopathy cell-based assays, Corr-2b was found to help restore localization of mutant dysferlin protein to the correct cellular location at the plasma membrane. The other compound, phenylbutyrate (4-PBA), was subsequently found to also be effective in restoring membrane localization to many known dysferlin mutants in vitro. In experiments in mice, 4-PBA was found to dramatically rescue membrane resealing following injury in DYSF-deficient cells. 4-PBA can act as a chemical chaperone to help some proteins fold properly, which may explain its ability to restore proper cellular localization of mutant dysferlin to help repair membrane damage.
Problem Addressed
Dysferlinopathy is caused by a mutation in the DYSF gene that results in a deficiency of the protein dysferlin, which repairs skeletal muscle membrane damage. Dysferlinopathy is characterized by gradually progressing muscle weakness and atrophy (wasting). These diseases significantly impact mobility, as patients usually lose the ability to walk unassisted between the ages of 40 and 45. Given that there is currently no cure or treatment specifically for dysferlinopathy, there is an urgent unmet need for the development of treatments. This technology describes active compounds that show promise for use in future treatments for dysferlinopath
Advantages
- Any treatment for dysferlinopathy derived from these compounds would likely be the first of its kind, as there is currently no dysferlinopathy-specific treatment.
- In vitro Corr-2b, particularly 4-PBA, shows the ability to restore proper cellular localization to DYSF mutants.
- 4-PBA is effective in in vivo mouse models and has a long record of safety in humans.
- Treatments developed for dysferlinopathy would fall under the category of orphan drugs, providing the developing company the associated benefits.
- Potential exists for other applications outside of dysferlinopathy, including treating muscle injuries, treating and preventing muscle loss, and promoting muscle growth.
Publications
Tominaga, K., N. Tominaga, E.O. Williams, et al. 2021. "4-Phenylbutyrate Restores Localization and Membrane Repair to Human Dysferlin Mutations." iScience 25, no. 1 (December 20): 103667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021.103667.
License this technology
Interested in this technology? Connect with our experienced licensing team to initiate the process.
Sign up for technology updates
Sign up now to receive the latest updates on cutting-edge technologies and innovations.