Antibody Mediated Delivery of Antigen to B Cell Follicles for Enhanced Humoral Response
This technology utilizes an antibody-based binding mechanism to specifically target vaccine antigens to the follicular dendritic cells (FDCs), a type of immune cells within the lymphoid follicle. This enables increased delivery of antigens to B-cells, a type of specialized white blood cells, for an enhanced immune response against infections.
Researchers
-
compositions and methods for antibody mediated delivery
of antigen to b cell follicles
United States of America | Pending
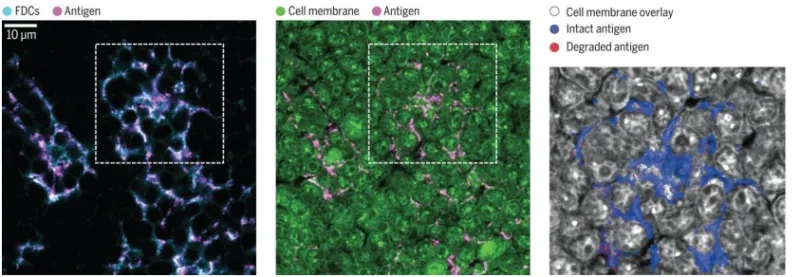
Figures
Technology
The technology is an immunizing protein comprised of an antigen and a binding mechanism. This binding mechanism specifically targets receptors expressed on the surface of the FDCs. The binding mechanism can be an antibody or some fragment thereof, ensuring effective binding to the target receptor on the FDC surface. This composition can be used as part of a prophylactic or therapeutic vaccine and with an adjuvant, which effectively enhances the body’s response to the antigen.
Problem Addressed
This technology utilizes a molecular binding mechanism to effectively target vaccine antigens to FDCs for long-lasting preservation of their structural integrity. Current approaches are limited by rapid antigen degradation in the lymph node which hinders the generation of protective antibodies by B-cells. This innovative method ensures the antigens remain intact and triggers an enhanced immune response. This is achieved by rapid antigen delivery to the FDCs and allows for a higher number of B-cells to recognize and respond to the intact antigens.
Current approaches for follicle-targeted immunizations depend on extensively coating invading antigens with plasma proteins to facilitate binding. By avoiding this protein coating step, this new technology promotes rapid follicular antigen localization by joining the antigen with a binding mechanism, thereby increasing immune response while circumventing the need for extensive protein deposition.
Advantages
-
The binding mechanism-antigen composition reduces the dosage and time required to induce, increase, or enhance an immune response.
-
The binding mechanism-antigen compositions can be used to induce an immune response when administering the antigen alone has been found ineffectual.
-
This composition achieves FDC targeting without the need for potent protein deposition on the pathogen, while still leading to significantly improved immune responses compared to non-follicle targeted counterparts.
Publications
Aung, A., et al. "Low Protease Activity in B Cell Follicles Promotes Retention of Intact Antigens after Immunization." Science (2022). Accessed February 14, 2022. PMID: 36701450. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abn8934.
License this technology
Interested in this technology? Connect with our experienced licensing team to initiate the process.
Sign up for technology updates
Sign up now to receive the latest updates on cutting-edge technologies and innovations.