Efficient and Reliable Transmission of Sparse Signals in Wireless Sensor Networks
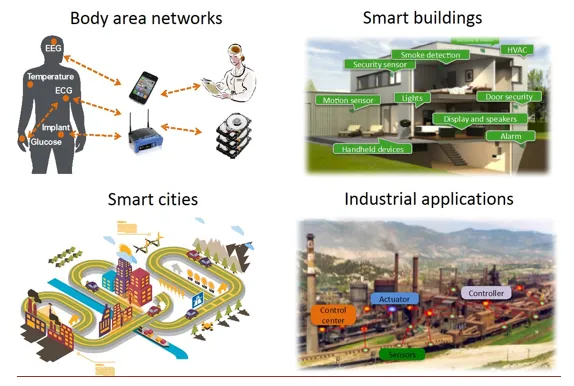
The invention is a low complexity architecture for communicating captured sparse signals in WSNs, with applications in health monitoring as well as industrial and consumer sector networks.
Researchers
-
methods, apparatus and systems for transmission and reception of sparse signals in wireless sensor networks
United States of America | Granted | 10,608,780
Figures
Technology
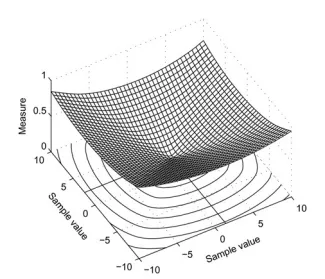
The application-independent physical layer design leverages sparsity existing in many physical signals to parsimoniously represent them. By preserving the relative bit importance during transmission, it achieves graceful tradeoffs between distortion and channel SNR, resulting in increased robustness against channel errors across a wide range of SNR values in a rateless fashion. The invention was proved to be optimal in terms of distortion in the high SNR regime in point-to-point links and can efficiently serve multicast scenarios. The device is applicable to a wide range of applications and performs close to an idealized layered transmission scheme in terms of reliability and end-to-end distortion.
Problem Addressed
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) are an emerging technology that will have a major societal, environmental and financial impact. By 2020, it is predicted that there will be more than 50 million interconnected nodes worldwide. WSNs seek to capture compressible analog signals and aim to transmit them reliably to one or more nodes, while maintaining low power consumption. Technical challenges include achieving communication reliability under delay constrains in harsh environments and limiting power consumption to ensure extended lifetimes. Current methods are often highly application specific. In addition, they do not work well in environments with unknown signal-to-noise (SNR) ratio, have limited performance in multiuser scenarios and lack feedback functionality.
Advantages
- Application and signal model independent communication architecture
- Simultaneous service of multiple receivers at their highest possible information rate
- No receiver feedback needed for optimal rate selection
- No computationally intense algorithms in transmitting sensor nodes
Publications
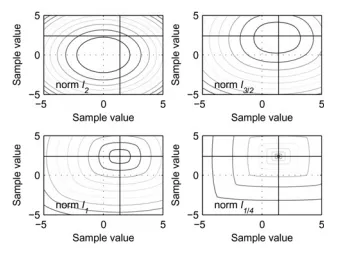
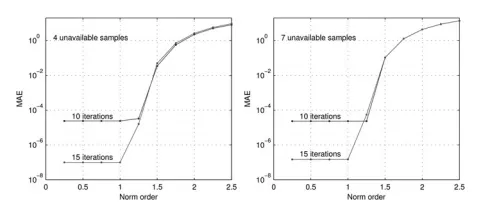
Stanković, Ljubiša, Miloš Daković, Stefan Vujović. "Adaptive Variable Step Algorithm for Missing Samples Recovery in Sparse Signals." First published on May 1, 2014. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2013.0385.
IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Prague, Czech Republic, May 22, 2011.
Angelopoulos, G., Médard, M., Chandrakasan, A. P. "AdaptCast: An Integrated Source to Transmission Scheme for Wireless Sensor Networks." Presented at the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), London, UK, 2015, pp. 2894-2899. doi: 10.1109/ICC.2015.7248766.
License this technology
Interested in this technology? Connect with our experienced licensing team to initiate the process.
Sign up for technology updates
Sign up now to receive the latest updates on cutting-edge technologies and innovations.