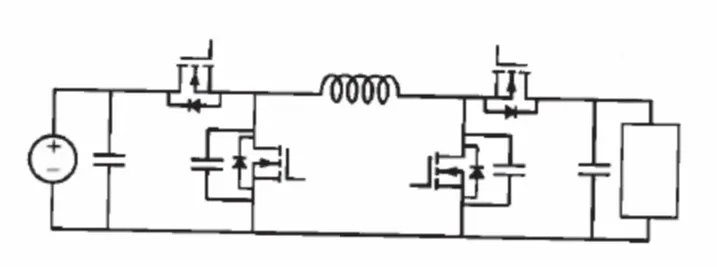
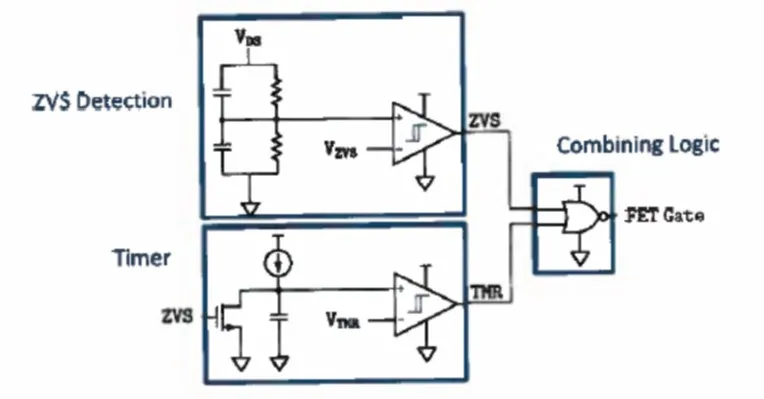
Wide-Operating-Range Resonant-Transition Soft-Switched Converter
This technology uses a soft switching technique in power converters to decrease energy loss during voltage conversion. The circuit topologies and control strategies of this invention are best suited for DC-DC power converters with large voltage/power ranges or AC-DC/DC-ACconverters which inherently must accommodate wide voltage/power ranges. The technology has particular advantages in AC-DC/DC-AC conversion, where the technology enables the use of a reduced dc link voltage (maintaining the advantages above), which benefits systems that interact with low-voltage sources or loads.
Researchers
-
wide-operating-range resonant-transition soft-switched converter
United States of America | Granted | 10,700,589
Figures
Technology
This technology employs soft switching circuits, switching patterns, and control methods to mitigate power loss in converters. In particular, the technology provides a technique to simultaneously achieve soft switching over a wide voltage and power range and accomplish this with low rms current and hence low conduction loss.
Control methods are used in the topology to maintain zero voltage switching. This means switches are either turned on with zero volts across or switched off with zero voltage and current. The soft switching technique avoids overlap losses because voltage is approximately zero during the transition period. Typically, power loss due to switches limits switching frequency and lowers power density. However, with this soft switching technique, zero loss leads to high switching frequency and high-power density, which achieves the technical requirements for large operating range converters.
Problem Addressed
Power systems with grid-connected electronic loads can lose twenty to seventy percent of energy during the voltage conversion process. Systems with wide voltage operating ranges are especially prone to high loss. A low power factor in power lines can also attribute to the energy loss in grid-connected systems. To address this challenge, converters must be capable of operating over a large operating range with high efficiency and high-power density.
Advantages
- Zero voltage switching during power conversion over wide operating ranges
- Mitigates power loss from parasitics (capacitance and inductance components) during power conversion
- Achieves both high efficiency and high-power density in large operating range converters
- Ability to operate with reduced dc-link voltage without losing advantages above
Publications
A. J. Hanson and D. J. Perreault, "A High-Frequency Power Factor Correction Stage With Low Output Voltage," in IEEE Journal of Emerging and Selected Topics in Power Electronics, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 2143-2155, Sept. 2020, doi: 10.1109/JESTPE.2019.2961853.
License this technology
Interested in this technology? Connect with our experienced licensing team to initiate the process.
Sign up for technology updates
Sign up now to receive the latest updates on cutting-edge technologies and innovations.