Novel Peptidic Agents for Targeting Chemoresistant Anti-Apoptotic Mcl-1
Mcl-1-binding peptides may be useful in treating a variety of chemotherapy-resistant cancers such as adult acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Researchers
-
selective mcl-1 binding peptides
United States of America | Published application -
selective mcl-1 binding peptides
United States of America | Pending
Figures
Technology
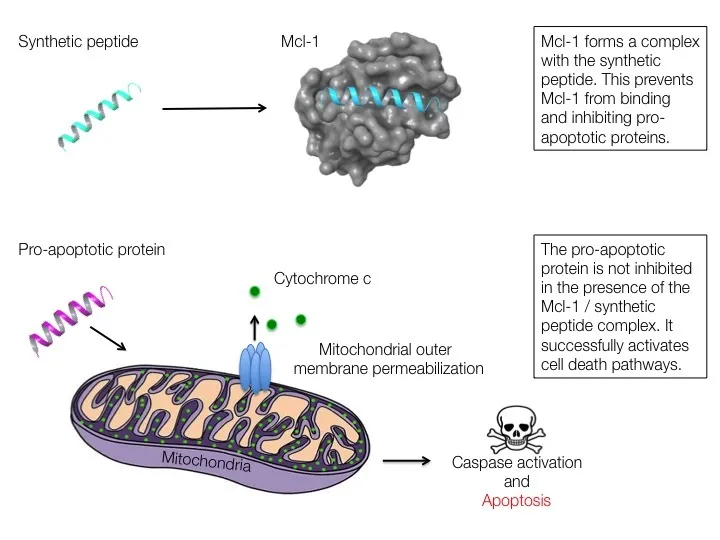
Mcl-1, along with other members of the Bcl-2 family, blocks apoptosis by binding to short helices in pro-apoptotic proteins, inhibiting their homo-oligomerization and activation. Synthetic peptides that bind Mcl-1 can be used to prevent this interaction by physically blocking the binding site on Mcl-1 and preventing its inhibition of pro-apoptotic proteins. This has been demonstrated using the short peptide MS1, which binds Mcl-1 and selectively induces mitochondrial permeabilization (MOMP) in Mcl-1-dependent cancer cells. This process has been improved upon with the use of hydrocarbon stapling to stabilize the peptide and promote its cellular uptake. Concurrently, a peptide library screen revealed two sequence modifications of MS1— each a substitution of an amino acid residue— that enhance binding to Mcl-1 without compromising a high degree of specificity or requiring hydrocarbon stapling for their activity. However, these high-affinity peptides still require a means for cell entry (e.g., nanoparticle delivery). In combination with a delivery system, the optimized peptides have therapeutic potential as highly selective Mcl-1 inhibitors.
Problem Addressed
Mcl-1 is an oncogene that is overexpressed in many cancers and confers resistance to chemotherapeutic agents. Mcl-1 belongs to a family of anti-apoptotic proteins with homology to B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2). Inhibition of Mcl-1 and related proteins using potent, selectively binding small molecules is a promising avenue for therapy; however, no such small molecule has been identified for Mcl-1. Synthetic peptides designed to selectively inhibit Mcl-1 are an alternative to small molecules. Upon delivery into the cell, the peptides bind and inhibit Mcl-1, making them candidates for development as cancer therapeutics.
Advantages
- High binding affinity
- Mcl-1 specific binding
Related Technologies
This case is related to MIT technology: #17695
Publications
Rezaei Araghi, R., Ryan, J. A., Letai, A., & Keating, A. E. (2016). Rapid Optimization of Mcl-1 Inhibitors using Stapled Peptide Libraries Including Non-Natural Side Chains. ACS Chemical Biology, 11(5), 1238-1244. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5b01002.
License this technology
Interested in this technology? Connect with our experienced licensing team to initiate the process.
Sign up for technology updates
Sign up now to receive the latest updates on cutting-edge technologies and innovations.